In global motion control supply chains, stepper motor lead time is a decisive factor influencing product launches, production scheduling, and overall project cost. We address this topic from a practical, manufacturing-driven perspective, clearly distinguishing standard stepper motor lead times from customized stepper motor lead times, while outlining the real variables that affect delivery accuracy, scalability, and reliability.
This guide is written for OEMs, system integrators, and procurement professionals who require predictable timelines and high-performance stepper motor solutions.
Besfoc Customized Stepper Motors
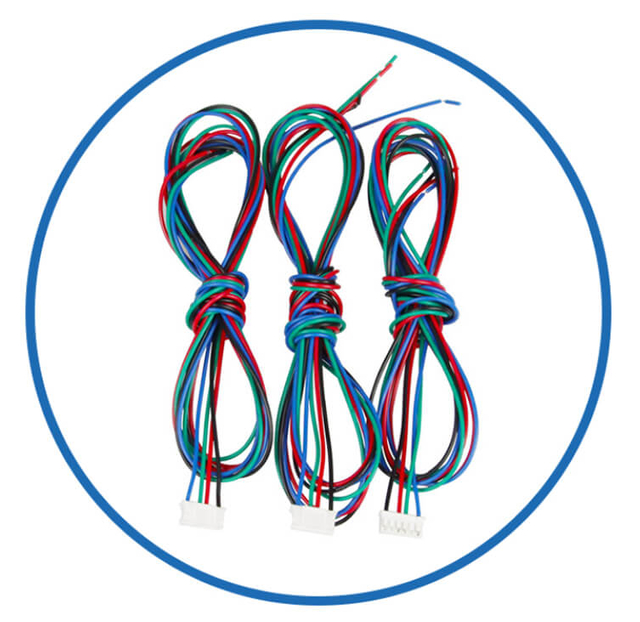 | 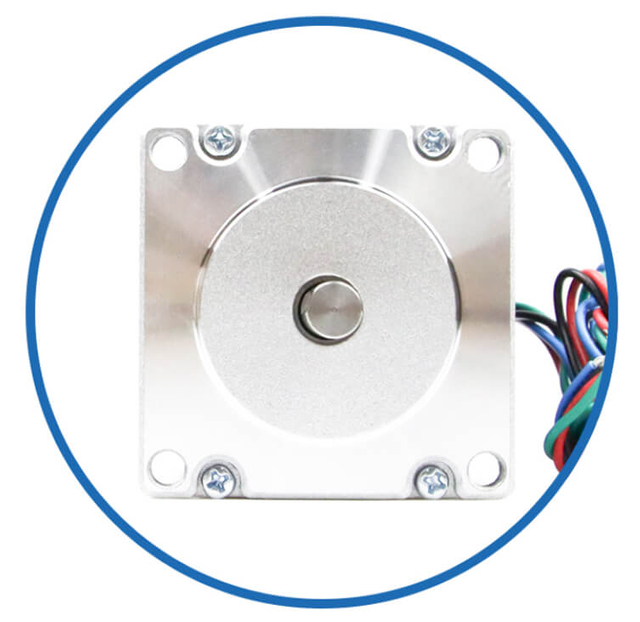 |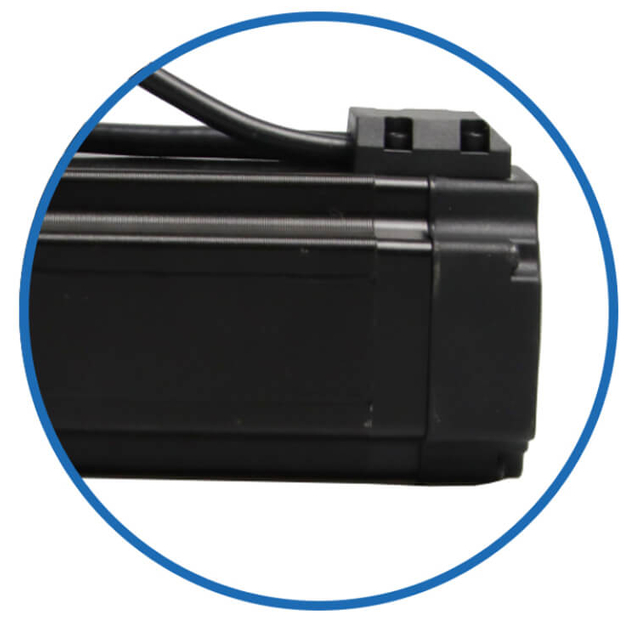  |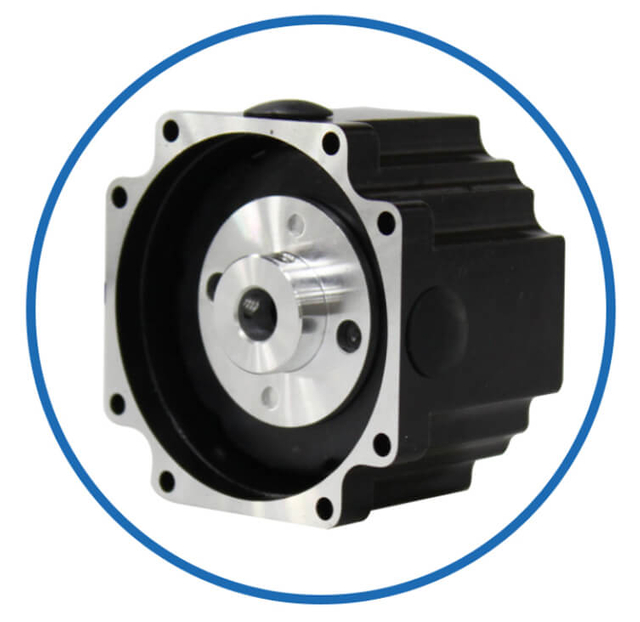  |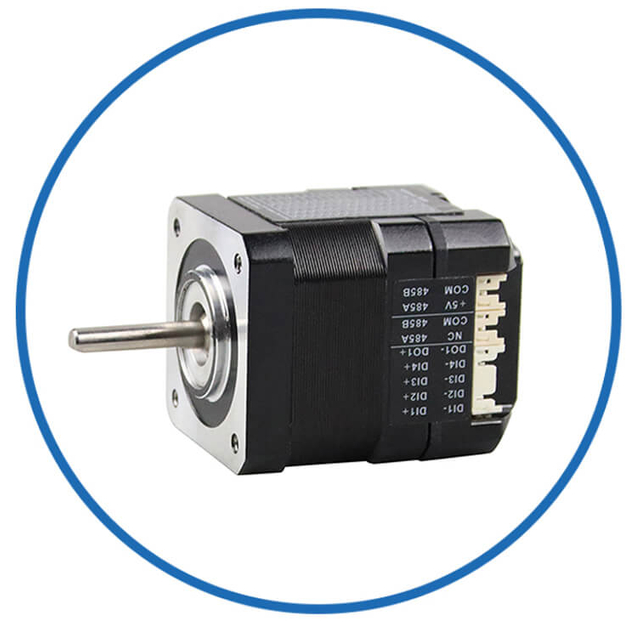  | BesFoc Customized Motors:
According to the application needs, provide a variety of customized motor solutions, common customization includes:
-
Sealed motor, suitable for dusty environment, dirty environment with small temperature change, etc
-
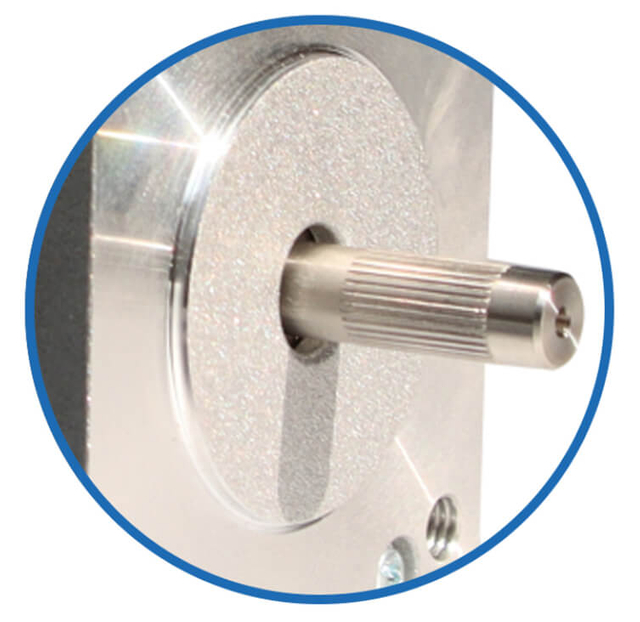
Special shaft, such as size, shape, etc
-
Belt wheels, gears and couplings etc
-
Encoders and other feedback components
-
Encoders and other feedback components. Lead length and customer use termination plug-in |
WIres Cables
| Stepper Motor Covers
| Closed Loop System
| Stepper Motor Brakes
| Integrated Systems
|
 |  |  |  |  |
Linear Actuator
| Motor Shaft
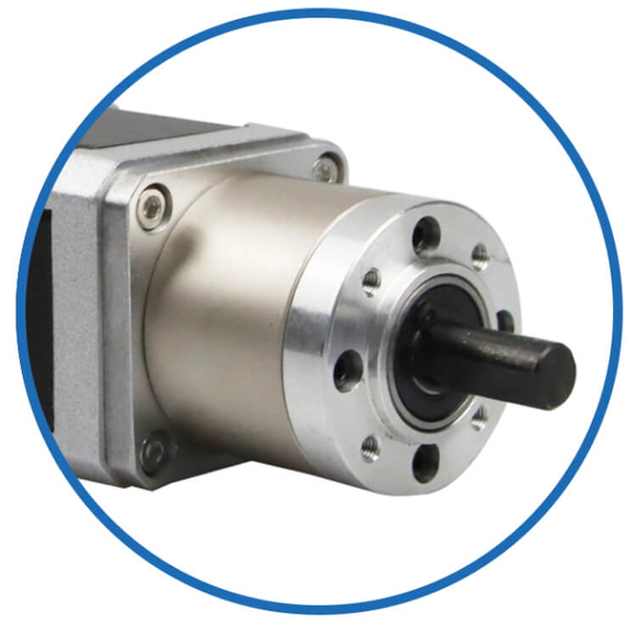
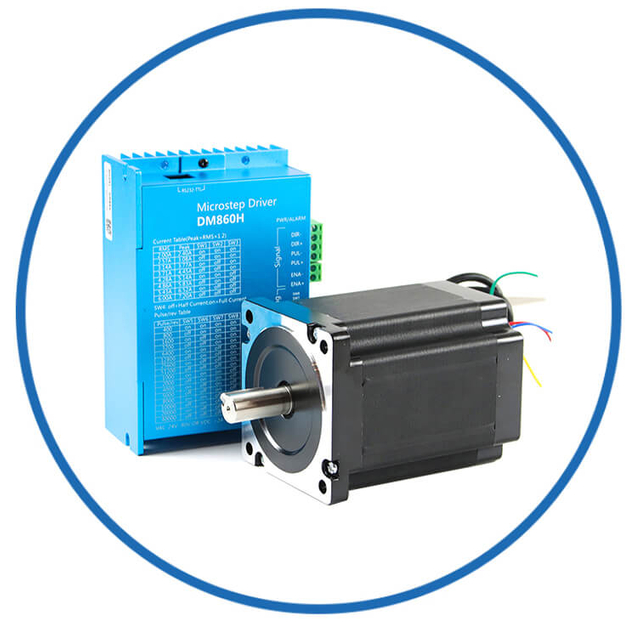
| Motor Gearbox | Driver System
| More Custom Service |
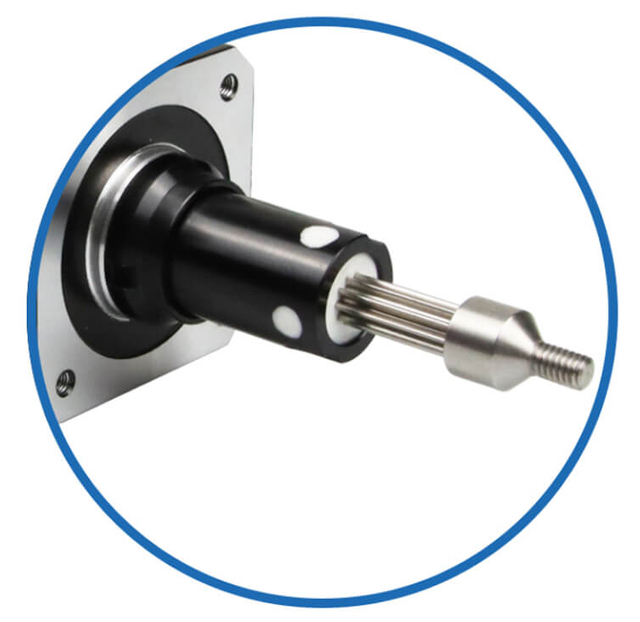
Besfoc Stepper Motor Shaft Customized Service
 | 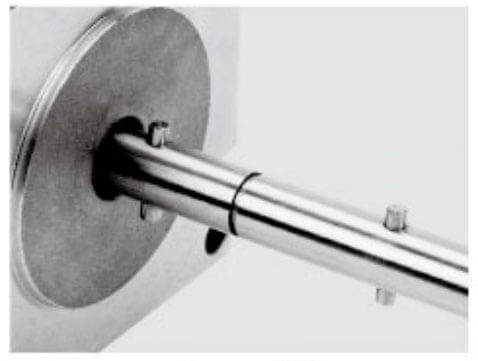 | 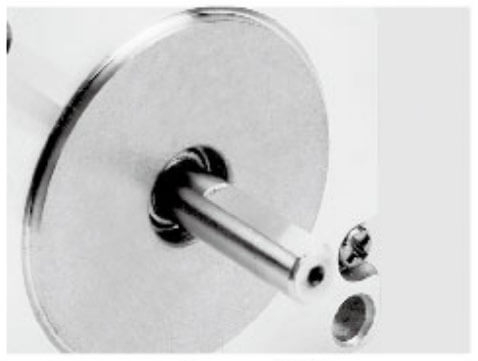 |  |  | 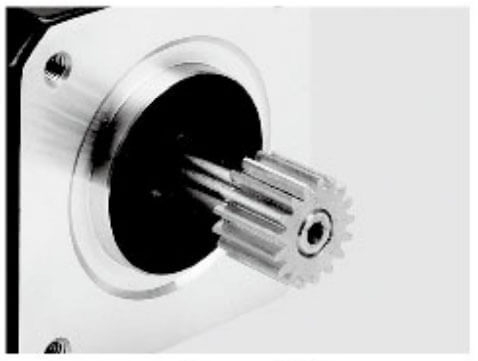 |
| Aluminum Pulley | Shaft Pin | Single D Shaft | Hollow Shaft | Plastic Pulley | Gear |
 | 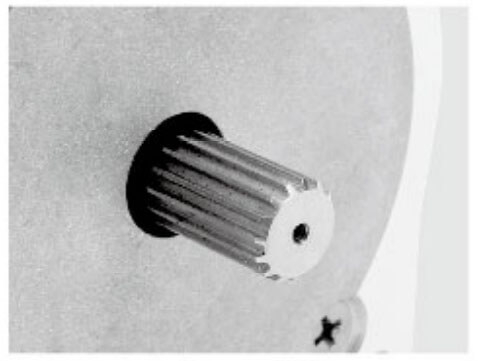 |  |  | 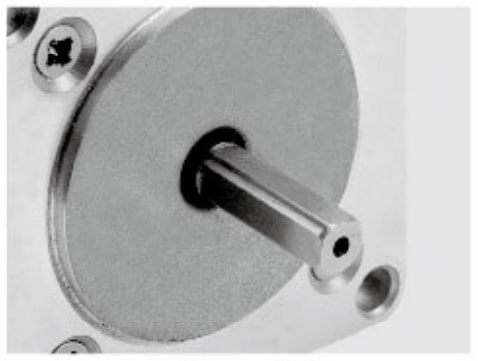 | 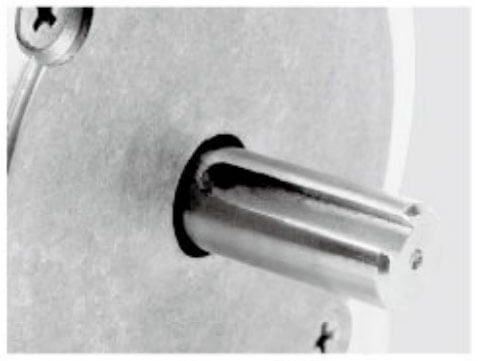 |
| Knurling | Hobbing Shaft | Screw Shaft | Hollow Shaft | Double D Shaft | Keyway |
What Lead Time Means in Stepper Motor Manufacturing
Stepper motor lead time refers to the total duration from order confirmation to shipment readiness. It includes:
Engineering review and order validation
Material procurement
Motor production and assembly
Testing and quality inspection
Packaging and dispatch preparation
Understanding these stages allows buyers to forecast schedules accurately and avoid costly delays.
Standard Stepper Motor Lead Time Overview
Definition of Standard Stepper Motors
Standard stepper motors are off-the-shelf models with predefined specifications, including:
Fixed frame sizes (NEMA 8, NEMA 11, NEMA 17, NEMA 23, NEMA 34)
Established winding parameters
Standard shaft dimensions
Common holding torque ratings
Industry-standard electrical interfaces
These motors are typically produced in high volume and stocked regularly.
Typical Lead Time for Standard Stepper Motors
For most manufacturers, standard stepper motor lead time ranges between:
The predictability of standard motor lead times makes them ideal for:
Key Factors That Enable Short Standard Lead Times
Short standard stepper motor lead times are not accidental; they are the result of mature manufacturing systems, optimized supply chains, and standardized engineering practices. We outline the core factors that consistently enable manufacturers to deliver standard stepper motors quickly and reliably.
Established Motor Platforms and Proven Designs
Standard stepper motors are built on well-established motor platforms that have been validated through years of mass production. Frame sizes, magnetic structures, winding configurations, and torque curves are already optimized and documented. Because no redesign or validation is required, production can begin immediately after order confirmation, eliminating engineering delays entirely.
High-Volume Raw Material Inventory
Manufacturers supporting short lead times maintain strategic inventory levels of critical raw materials, including stator laminations, rotor stacks, copper wire, bearings, and housings. These materials are purchased in bulk and stored based on historical demand forecasts, allowing production to proceed without waiting for supplier replenishment. This inventory readiness is one of the strongest contributors to fast delivery cycles.
Automated and Dedicated Production Lines
Standard stepper motors benefit from highly automated production lines designed for repeatability and speed. Automated winding machines, precision assembly stations, and inline testing systems minimize manual intervention and reduce variability. Dedicated lines for popular models ensure consistent throughput and prevent bottlenecks caused by frequent line changeovers.
Pre-Approved Bills of Materials (BOMs)
All components used in standard motors are governed by pre-approved BOMs. Every part has a fixed specification, qualified supplier, and stable cost structure. This eliminates sourcing ambiguity, reduces procurement lead time, and ensures uninterrupted material flow into production.
Streamlined Quality Control Processes
Quality control for standard motors follows routine inspection protocols rather than application-specific testing. Standardized electrical, mechanical, and dimensional checks are performed quickly using predefined acceptance criteria. Because performance characteristics are already validated, no extended testing cycles are required.
Predictable Production Scheduling
Consistent demand patterns allow manufacturers to plan predictable production schedules for standard stepper motors. Forecast-based planning enables batch production ahead of confirmed orders, further compressing lead times and enabling rapid shipment once orders are placed.
Stable Supplier Ecosystem
Short lead times are reinforced by a stable and long-term supplier network. Trusted suppliers provide components with consistent quality and delivery performance, reducing the risk of delays caused by material shortages or requalification issues.
Minimal Order Processing Complexity
Standard motor orders require minimal documentation, no drawing approvals, and no parameter confirmation cycles. This simplified order processing accelerates internal workflows from sales to production, allowing factories to respond quickly to customer demand.
Together, these factors create a manufacturing environment where standard stepper motor lead times remain short, predictable, and scalable, making them the preferred choice for time-sensitive and high-volume applications.
Customized Stepper Motor Lead Time Explained
What Qualifies as a Customized Stepper Motor
A custom stepper motor involves any modification beyond standard catalog specifications, such as:
Custom winding resistance or inductance
Non-standard voltage or current ratings
Special shaft geometry or length
Integrated gearbox or brake
Encoder integration (incremental or absolute)
Custom mounting flanges
Extended temperature range or IP protection
Each customization introduces additional production steps.
Typical Lead Time for Customized Stepper Motors
Customized stepper motor lead time generally falls within:
15–30 working days for light customization
30–45 working days for complex mechanical or electrical modifications
45–60+ working days for fully bespoke designs requiring tooling
The timeline depends on design complexity, approval cycles, and testing requirements.
Engineering and Validation Phase Impact on Lead Time
Unlike standard motors, customized orders require:
Technical feasibility analysis
Electromagnetic simulation and torque validation
Mechanical drawing confirmation
Sample prototyping
Customer approval before mass production
This engineering front-end typically adds 7–14 days before production even begins.
Material Procurement and Custom Component Delays
Customized motors often require non-standard materials, including:
Special-grade silicon steel laminations
Custom shaft machining
Unique connectors or cables
High-temperature insulation materials
If these components are not in stock, procurement alone may extend lead time by 10–20 working days.
Production Complexity and Batch Size Considerations
Low MOQ Custom Orders
Small-batch customized motors usually have longer lead times because:
Production line changeovers are required
Manual assembly replaces automation
Dedicated testing procedures are necessary
Low MOQ orders prioritize precision over speed.
High-Volume Custom Orders
For large-volume customized projects, lead time improves after initial setup because:
Once validated, repeat orders typically see lead time reduced by 20–30%.
Quality Control and Testing Requirements
Customized stepper motors undergo expanded inspection, including:
Torque curve verification
Thermal rise testing
Insulation resistance testing
Encoder signal validation
Noise and vibration analysis
These steps ensure application-specific reliability but add measurable time to delivery schedules.
Comparison Table: Standard vs Customized Stepper Motor Lead Time
| Category | Standard Stepper Motor | Customized Stepper Motor |
| Engineering Review | Not required | Mandatory |
| Tooling | Existing | May be required |
| Material Sourcing | Stocked | Partially custom |
| Lead Time Range | 3–15 days | 15–60+ days |
| MOQ | Low | Flexible but higher |
| Unit Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Performance Optimization | Limited | High |
How Manufacturers Reduce Customized Lead Time
Reducing customized stepper motor lead time is a priority for experienced manufacturers serving OEM and industrial automation markets. While custom designs inherently require more processing than standard models, leading factories apply structured methods to shorten delivery cycles without sacrificing performance or quality.
Modular Motor Platform Design
Manufacturers develop modular stepper motor platforms where key components—such as stators, rotors, housings, and end caps—are standardized. Customization is achieved by combining pre-qualified modules rather than creating entirely new designs. This approach significantly reduces engineering and tooling time.
Pre-Engineered Customization Options
Instead of fully bespoke development, manufacturers offer pre-engineered customization ranges, including selectable winding parameters, shaft lengths, connector types, and mounting options. These predefined choices minimize design iterations and accelerate order confirmation.
Parallel Engineering and Procurement
Advanced manufacturers run engineering validation and material procurement in parallel. While electrical and mechanical parameters are being finalized, long-lead raw materials such as laminations, shafts, or special insulation are sourced simultaneously, preventing idle waiting periods.
Semi-Finished Component Inventory
Maintaining stock of semi-finished components—such as unwound stators, pre-machined shafts, and motor housings—allows rapid final assembly once customization details are confirmed. This strategy cuts weeks from traditional build-from-scratch timelines.
Parametric Winding Libraries
By using parametric winding databases, manufacturers can quickly configure torque, current, and voltage characteristics without extensive re-engineering. Proven winding combinations reduce testing time and eliminate trial-and-error production.
Rapid Prototyping and Validation
Efficient factories deploy fast prototype lines and streamlined testing procedures to validate custom motors quickly. Accelerated torque testing, thermal analysis, and electrical verification enable faster approval for mass production.
Dedicated Custom Production Lines
Some manufacturers operate dedicated low-volume or custom production lines, preventing custom orders from being delayed by high-volume standard motor production. This separation improves scheduling accuracy and shortens delivery timelines.
Clear Technical Communication
Early and precise technical communication reduces revisions. When customers provide complete drawings, performance targets, and environmental conditions upfront, manufacturers can avoid redesign loops that typically extend lead time.
Through modular design, smart inventory management, and streamlined engineering workflows, manufacturers are able to reduce customized stepper motor lead time while still delivering application-specific performance and long-term reliability.
How to Choose Between Standard and Customized Motors
We recommend selecting standard stepper motors when:
Application requirements align with catalog specs
Speed-to-market is critical
Cost control is a priority
We recommend customized stepper motors when:
Performance optimization is essential
Space or torque constraints exist
Integration with encoders or gearboxes is required
Long-term product differentiation matters
Strategic Planning for Stepper Motor Lead Time
Effective strategic planning for stepper motor lead time is essential for maintaining production continuity, controlling costs, and meeting market launch schedules. We approach lead time planning as a proactive process that aligns technical requirements, supply chain readiness, and manufacturing capacity from the earliest project stage.
Early Definition of Technical Specifications
Clear and complete definition of electrical and mechanical specifications at the outset significantly reduces lead time risk. Key parameters such as voltage, current, holding torque, step angle, shaft configuration, mounting dimensions, and environmental conditions must be finalized before order placement. Early specification stability prevents redesign cycles that delay production start.
Accurate Demand Forecasting and Volume Planning
Reliable demand forecasts allow manufacturers to allocate capacity and reserve materials in advance. By communicating expected order quantities, annual volumes, and ramp-up schedules, buyers enable factories to plan production slots efficiently, minimizing queue time and avoiding capacity constraints during peak demand periods.
Selecting the Right Motor Type Early
Choosing between standard stepper motors and customized stepper motors early in the design phase is critical. Standard motors support short and predictable lead times, while customized motors require extended planning due to engineering validation and specialized sourcing. Early motor type selection ensures realistic delivery expectations and avoids late-stage design compromises.
Supplier Capability Assessment
Strategic planning includes evaluating the manufacturer's engineering strength, production scalability, and supply chain resilience. Manufacturers with modular designs, in-house winding, and machining capabilities are better positioned to manage both standard and custom lead times efficiently. This assessment reduces dependency risks and improves delivery reliability.
Parallel Engineering and Procurement Planning
For customized projects, lead time is optimized by running engineering review and material procurement in parallel rather than sequentially. Early identification of long-lead components, such as custom shafts or special insulation materials, allows procurement to begin before final design approval, compressing the overall schedule.
Prototype and Sample Validation Scheduling
Allocating sufficient time for sample production, testing, and approval is a vital element of lead time strategy. Structured validation schedules with predefined acceptance criteria prevent repeated revisions and accelerate transition from prototype to mass production.
Buffer Time and Risk Mitigation Planning
Incorporating buffer time into the project timeline protects against unforeseen disruptions such as material shortages, logistics delays, or quality rework. Strategic buffers ensure that downstream assembly and product launches remain unaffected even if minor delays occur.
Clear Communication and Change Control
Effective lead time management depends on disciplined change control procedures. Any modification to specifications, quantities, or delivery requirements must be evaluated for its impact on lead time. Clear communication channels between engineering, procurement, and manufacturing teams prevent misalignment and schedule slippage.
Long-Term Supplier Collaboration
Building long-term partnerships with stepper motor manufacturers enables shared forecasting, capacity planning, and continuous lead time improvement. Strategic collaboration supports priority production scheduling, flexible MOQ arrangements, and faster response times for repeat orders.
Through disciplined planning, early alignment, and structured execution, strategic planning for stepper motor lead time transforms delivery timelines into a predictable and controllable component of the overall production strategy.
Conclusion: Managing Stepper Motor Lead Time with Confidence
Understanding the differences between standard and customized stepper motor lead times enables smarter procurement decisions and smoother production schedules. Standard motors deliver speed and predictability, while customized motors offer performance precision at the cost of extended timelines. By partnering with capable manufacturers and planning specifications early, lead time becomes a controlled variable rather than a risk factor.
FAQs About Stepper Motor Lead Time
I. Product Perspective: Stepper Motor Lead Time & Product Factors
1. What does lead time mean when ordering a customized stepper motor?
Lead time refers to the total time a stepper motor manufacturer needs to produce and deliver a customized stepper motor, from order confirmation to shipment.
2. What is the typical lead time for a customized stepper motor?
For most customized stepper motors, lead time typically ranges from a few weeks depending on customization complexity and production volume.
3. How does motor type affect stepper motor lead time?
Standard hybrid stepper motors usually have shorter lead times, while customized stepper motors such as linear or closed-loop types require longer production time.
4. Do standard stepper motors have shorter lead times than custom ones?
Yes, standard products from a stepper motor manufacturer are often in stock or produced faster than fully customized models.
5. Does stepper motor frame size impact lead time?
Yes, smaller frame sizes like NEMA 8 or NEMA 17 often have shorter lead times than large or high-torque stepper motors.
6. How does quantity affect stepper motor lead time?
Larger order quantities may extend lead time, especially for customized stepper motors requiring additional material preparation.
7. Does adding a gearbox increase lead time?
Yes, integrating planetary or worm gearboxes usually increases the lead time of a customized stepper motor.
8. Are linear stepper motors slower to manufacture?
Yes, linear and non-standard designs often require additional machining, increasing lead time from the stepper motor manufacturer.
9. Can stepper motor lead time be reduced for urgent projects?
Some stepper motor manufacturers offer expedited production options for urgent customized stepper motor orders.
10. How does quality testing affect lead time?
Custom products undergo additional testing, which slightly increases lead time but ensures reliability and performance.
II. Factory Customization Capability: Manufacturing & Supply Chain Factors
11. How does customization level impact lead time at a stepper motor manufacturer?
Minor changes like shaft length require less time, while new tooling significantly increases customized stepper motor lead time.
12. Can using existing motor platforms reduce lead time?
Yes, many stepper motor manufacturers reduce lead time by modifying existing motor platforms instead of building from scratch.
13. Does encoder integration affect lead time?
Yes, adding encoders or closed-loop control increases lead time for customized stepper motors.
14. How do material availability and supply chain affect lead time?
Availability of laminations, magnets, and electronics directly impacts production schedules at a stepper motor manufacturer.
15. Can prototype samples be delivered faster than mass production?
Yes, prototype customized stepper motors are usually produced faster than bulk orders.
16. How can OEM buyers help reduce stepper motor lead time?
Providing clear specifications and forecasts helps a stepper motor manufacturer shorten lead time.
Yes, ODM solutions often require longer lead times than OEM customized stepper motors.
18. How does factory automation influence lead time?
Highly automated stepper motor manufacturers can reduce lead time while maintaining quality.
19. Can long-term cooperation reduce future lead times?
Yes, stable partnerships allow stepper motor manufacturers to plan production and shorten lead time for repeat orders.
20. Why is lead time transparency important when choosing a stepper motor manufacturer?
Transparent lead time helps buyers plan inventory, reduce risk, and ensure timely delivery of customized stepper motors.
English
العربية
Français
Русский
Español
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
ພາສາລາວ
ភាសាខ្មែរ
Bahasa Melayu
ဗမာစာ
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
Latine
Dansk
Shqip
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
Azərbaycan dili
Български
Català
































