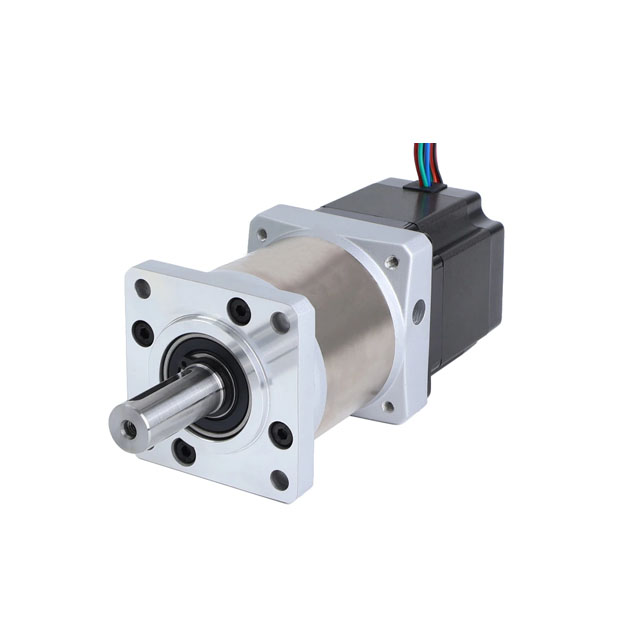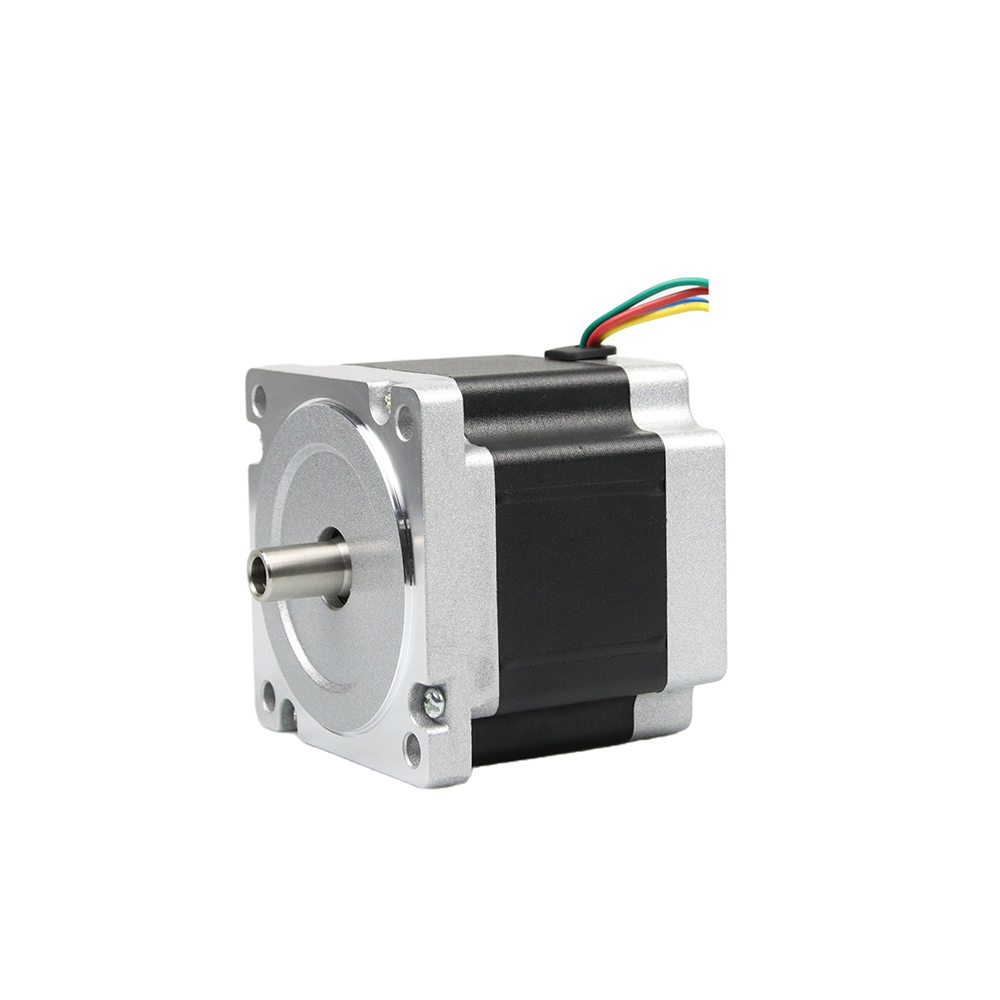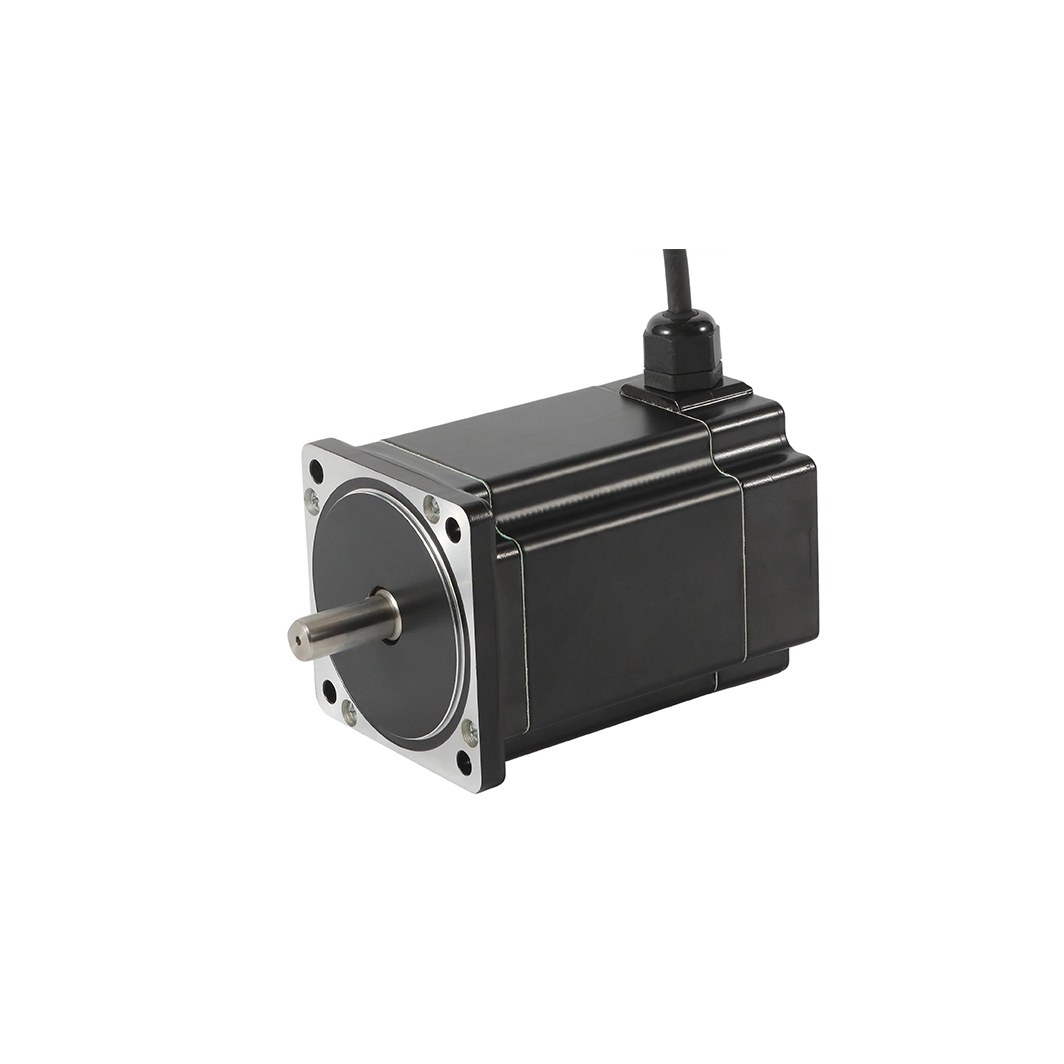
Understanding MOQ in the Context of Custom Stepper Motors
In the global motion control industry, Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) plays a decisive role in sourcing custom stepper motors from China manufacturers. We recognize that MOQ is not merely a purchasing threshold; it is a strategic lever that affects cost structure, production efficiency, lead time, and long-term supply stability. When working with Chinese factories, MOQ is shaped by engineering customization, material procurement, tooling investment, and production planning. Understanding these dynamics enables buyers to negotiate effectively and align orders with business objectives.
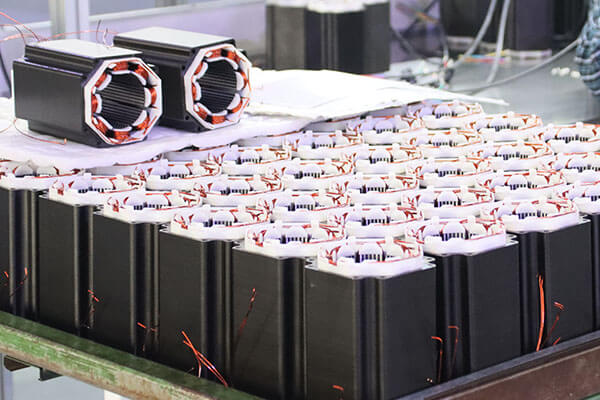
Besfoc Customized Stepper Motors
 |  |  |  |  | BesFoc Customized Motors:
According to the application needs, provide a variety of customized motor solutions, common customization includes:
-
Sealed motor, suitable for dusty environment, dirty environment with small temperature change, etc
-
Special shaft, such as size, shape, etc
-
Belt wheels, gears and couplings etc
-
Encoders and other feedback components
-
Encoders and other feedback components. Lead length and customer use termination plug-in |
WIres Cables
| Stepper Motor Covers
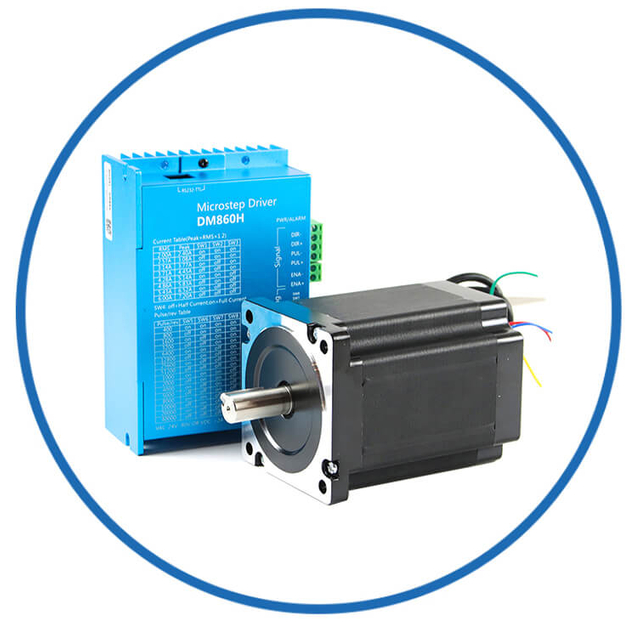
| Closed Loop System
| Stepper Motor Brakes
| Integrated Systems
|
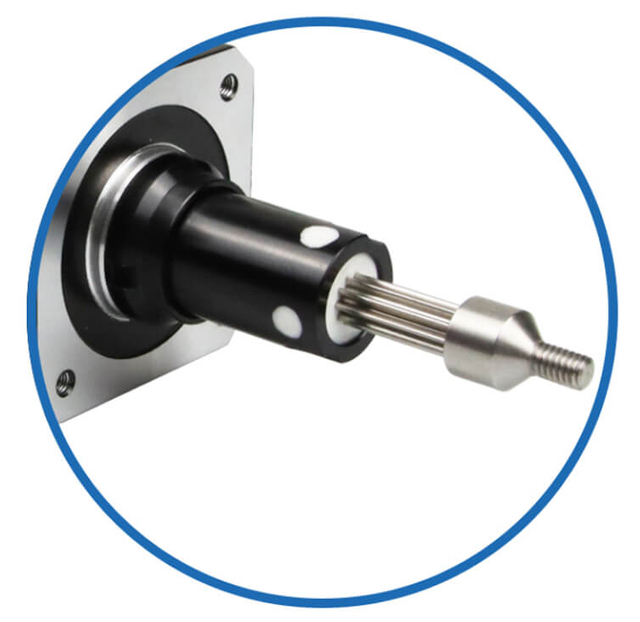 |  |  |  |  |
Linear Actuator
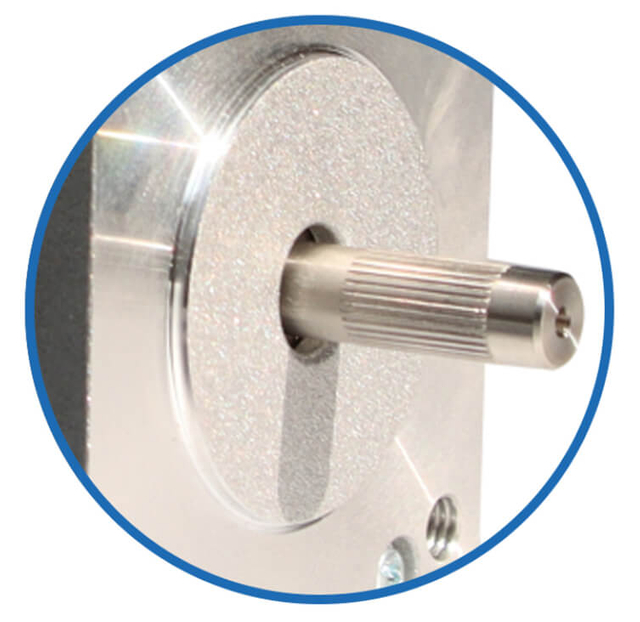
| Motor Shaft
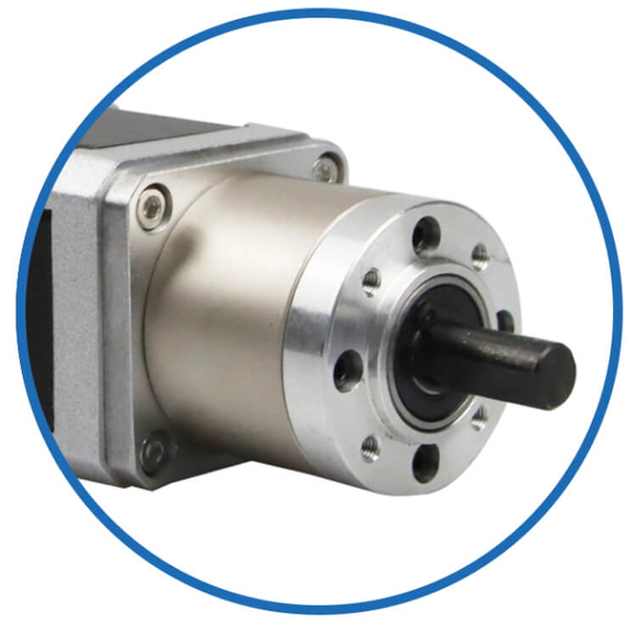
| Motor Gearbox | Driver System
| More Custom Service
|
Besfoc Stepper Motor Shaft Customized Service
 |  |  |  |  | 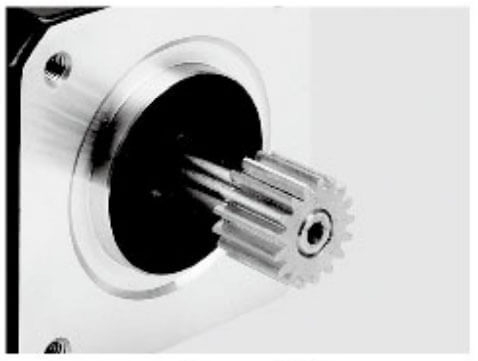 |
| Aluminum Pulley | Shaft Pin | Single D Shaft | Hollow Shaft | Plastic Pulley | Gear |
 | 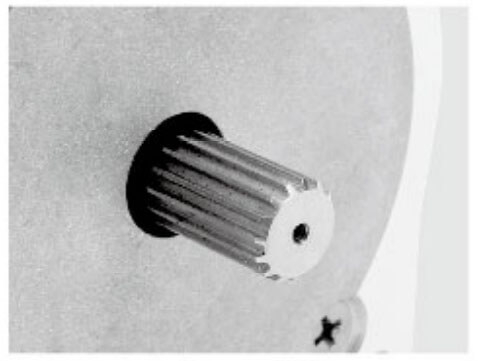 |  |  | 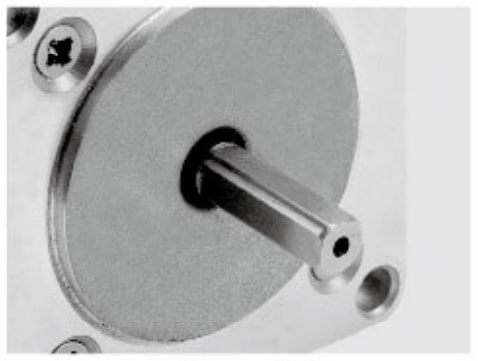 | 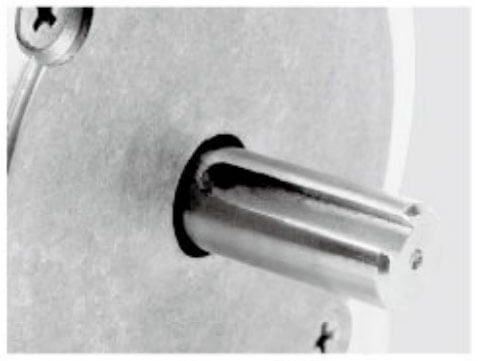 |
| Knurling | Hobbing Shaft | Screw Shaft | Hollow Shaft | Double D Shaft | Keyway |
Typical MOQ Ranges for Custom Stepper Motors
For custom stepper motors from China, typical MOQ ranges vary based on the degree of customization:
Minor customization (shaft length, connector type, cable length, label): 50–200 units
Moderate customization (winding parameters, holding torque, voltage/current tuning): 300–1,000 units
Full customization (new stator/rotor design, housing, magnetic circuit, tooling): 1,000–5,000 units or more
We observe that many reputable China manufacturers offer flexible MOQs for pilot runs, especially when long-term cooperation or annual volume forecasts are provided.
Key Factors That Determine MOQ for Custom Stepper Motors
The Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) for custom stepper motors is not arbitrary. It is determined by a combination of engineering, manufacturing, and supply-chain realities. Understanding these factors allows buyers to evaluate supplier quotations accurately and make informed sourcing decisions.
Level of Customization Required
The most influential factor is the degree of customization. Simple modifications—such as shaft length, connector type, cable orientation, or labeling—can usually be accommodated with a low MOQ. However, when customization involves custom windings, torque optimization, special voltage/current ratings, or unique mechanical dimensions, the MOQ increases because production processes must be adjusted specifically for that design.
Tooling and Non-Recurring Engineering (NRE) Costs
Custom stepper motors often require new tooling, including fixtures, molds, winding programs, or testing jigs. These one-time engineering investments must be amortized across the production volume. A higher MOQ helps manufacturers spread these costs efficiently, directly influencing the minimum quantity they are willing to accept.
Raw Material Procurement Constraints
Stepper motor production relies on electrical steel laminations, copper wire, bearings, and permanent magnets. When custom specifications require non-standard materials, manufacturers must meet their own suppliers’ minimum purchase quantities. These upstream constraints frequently define the MOQ for the final motor assembly.
Motor Size and Power Rating
Larger frame sizes and higher-torque motors generally carry higher MOQs. High-power stepper motors use thicker copper wire, larger laminations, and stronger magnets, all of which increase material costs and production complexity, making small batch runs less economical.
Production Line Setup and Efficiency
Manufacturers design their production lines for batch efficiency and process stability. Each design change requires setup time, calibration, and validation. To maintain quality consistency and acceptable yields, factories often set MOQs that align with optimal batch sizes.
Quality Control and Testing Requirements
Custom motors typically require enhanced testing, such as torque verification, thermal testing, noise analysis, or endurance validation. These procedures add time and labor costs, which are more cost-effective when spread across a larger production quantity, thereby influencing MOQ levels.
Integration of Additional Components
When stepper motors are combined with gearboxes, encoders, brakes, or integrated drivers, MOQ is affected by the availability and minimum order requirements of these additional components. Multi-component assemblies almost always require higher MOQs than standalone motors.
Supplier Capacity and Business Model
Manufacturers focused on OEM and industrial customers typically set higher MOQs compared to factories that specialize in prototypes or low-volume customization. The factory’s production capacity, automation level, and target market segment all play a role in defining acceptable order quantities.
Forecasted Order Volume and Long-Term Cooperation
Factories are often willing to reduce initial MOQ if buyers provide credible annual demand forecasts or commit to long-term cooperation. Future volume potential can significantly offset the risk of low initial orders.
Market Demand and Standardization Level
Highly standardized stepper motor models benefit from shared components and stable demand, enabling lower MOQs. Conversely, niche or application-specific designs with limited market demand usually require higher MOQs to justify production resources.
MOQ Differences by Stepper Motor Type
For hybrid stepper motors (NEMA 8–NEMA 42), typical MOQs range from 200 to 1,000 units depending on torque class and customization depth. Hybrid motors benefit from mature supply chains, enabling relatively lower MOQs.
Permanent Magnet Stepper Motors
PM stepper motors often carry higher MOQs due to specialized magnet tooling and lower overall market volume. Expect 500–2,000 units for custom designs.
Closed-loop stepper motors with encoders and drivers involve multi-component integration. MOQs generally start at 300–1,000 sets, influenced by encoder sourcing and firmware configuration.
For stepper motors with gearboxes, MOQs depend on gearbox type (planetary, spur, worm). Combined assemblies typically require 500–1,500 units, particularly when custom gear ratios or housings are involved.
MOQ vs. Unit Price: The Cost Optimization Balance
We consistently find a direct correlation between MOQ and unit pricing. Higher MOQs unlock:
Lower material costs through bulk procurement
Reduced setup cost per unit
Improved yield and consistency
More aggressive pricing tiers
Conversely, low MOQs may carry engineering surcharges or price premiums, which can be strategically acceptable during prototyping or market validation phases.
How China Manufacturers Support Low MOQ Projects
Leading China stepper motor manufacturers have evolved to support low-MOQ custom projects through:
Modular motor platforms that allow customization without new tooling
Stock semi-finished components enabling rapid configuration
Shared tooling strategies across similar motor families
Engineering support for design-for-manufacturing (DFM) to reduce MOQ requirements
These capabilities make China a preferred sourcing destination for startups, SMEs, and OEMs requiring flexibility.
MOQ Negotiation Strategies That Deliver Results
Leverage Annual Volume Forecasts
Presenting a 12–24 month demand forecast often persuades manufacturers to approve lower initial MOQs while planning scalable production.
Start with Engineering Samples
Most factories accept sample orders (5–20 units) before mass production. While samples carry higher unit costs, they significantly reduce project risk.
Accept Partial Customization
By aligning designs with existing motor frames, laminations, or windings, buyers can dramatically reduce MOQ thresholds.
Bundle Multiple SKUs
Combining similar custom motors into a consolidated order increases total volume, helping meet MOQ requirements without excess inventory.
MOQ Expectations by Buyer Profile
Startups and R&D Teams
MOQs of 50–300 units are achievable when customization is limited and future scaling is clearly communicated.
For OEM applications, MOQs of 500–2,000 units are standard, balancing customization depth with cost efficiency.
High-Volume Industrial Buyers
Large buyers typically commit to 3,000–10,000 units, securing the best pricing, priority production slots, and long-term supply agreements.
Quality Assurance and MOQ Considerations
Lower MOQs do not imply compromised quality. Reputable China manufacturers maintain consistent IQC, IPQC, and OQC standards regardless of order size. However, adequate MOQ ensures:
We advise aligning MOQ decisions with application criticality, especially in medical, automation, and aerospace-adjacent sectors.
Lead Time Implications of MOQ
The Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) has a direct and measurable impact on the lead time of custom stepper motors. From engineering preparation to final shipment, MOQ influences how quickly a manufacturer can allocate resources, schedule production, and deliver finished motors. Understanding this relationship helps buyers plan procurement cycles more accurately and avoid unexpected delays.
Engineering Preparation and Pre-Production Timing
For low-MOQ orders, manufacturers often prioritize engineering validation over production speed. Custom designs with small quantities require the same level of drawing approval, process setup, and performance verification as high-volume orders, but without the benefit of scale. This can extend the pre-production phase, especially when engineering resources are shared across multiple projects.
Material Procurement Lead Time
MOQ directly affects how quickly raw materials can be sourced. Higher MOQs enable bulk purchasing of laminations, copper wire, magnets, and bearings, which are often available from stock or preferred suppliers. In contrast, low-MOQ orders may require special material purchases that take longer to procure, increasing overall lead time before production can begin.
Production Scheduling Priority
Manufacturers typically schedule production in large, continuous batches to maximize efficiency. Orders that meet or exceed standard MOQ thresholds are easier to integrate into production plans and often receive higher scheduling priority. Small-quantity orders may need to wait for compatible production windows, leading to longer queue times.
Setup and Changeover Efficiency
Each custom stepper motor design requires line setup, parameter calibration, and trial runs. For low MOQs, the setup time represents a larger proportion of the total production cycle, making manufacturers less inclined to interrupt ongoing runs. As a result, low-MOQ orders may experience delayed start times compared to higher-volume orders.
Testing and Quality Assurance Duration
Custom motors often undergo enhanced inspection and functional testing. While testing standards remain consistent regardless of quantity, higher MOQs allow testing to be performed in parallel or through automated systems. Low-MOQ projects may rely more on manual testing, which can extend quality assurance lead times.
Component Integration and Assembly Delays
For stepper motors integrated with gearboxes, encoders, or drivers, MOQ influences the availability of these components. Higher quantities improve coordination across multiple suppliers, while small orders may wait for component consolidation, adding extra days or weeks to the delivery schedule.
Logistics and Shipment Planning
MOQ also affects outbound logistics. Large orders benefit from consolidated shipments, optimized packaging, and pre-booked freight options. Low-MOQ orders may ship less frequently or wait for consolidation, slightly extending total delivery time even after production is complete.
Typical Lead Time Ranges by MOQ
Prototype and sample orders (5–20 units): 7–15 days
Low-MOQ custom production (50–300 units): 20–30 days
Standard MOQ production (500–1,000 units): 25–40 days
High-volume production (3,000+ units): 30–45 days with stable scheduling
Strategic Planning to Reduce Lead Time
Aligning design choices with existing motor platforms, consolidating orders, and providing forecasted volumes can significantly shorten lead times even when MOQ is modest. Clear technical documentation and fast approval cycles further reduce delays at the engineering stage.
In practical terms, MOQ is a key driver of lead time predictability. Buyers who align order quantities with manufacturing realities benefit from faster production starts, smoother scheduling, and more reliable delivery timelines for custom stepper motors.
Long-Term Benefits of Strategic MOQ Planning
A well-structured MOQ strategy delivers:
Predictable supply chains
Lower total cost of ownership
Improved supplier commitment
Faster ownership
Improved supplier commitment
Faster iteration cycles for future designs
We consistently see buyers who plan MOQs strategically achieve superior outcomes in performance, pricing, and partnership stability.
Conclusion: Defining the Right MOQ for Custom Stepper Motors
The typical MOQ for custom stepper motors from a China manufacturer is not a fixed number but a calculated outcome of customization level, production economics, and partnership strategy. By understanding MOQ drivers and engaging manufacturers with clarity and foresight, buyers secure optimal pricing, reliable quality, and scalable supply. China’s manufacturing ecosystem remains uniquely positioned to deliver flexible MOQs, engineering depth, and global competitiveness for custom stepper motor solutions.
FAQs About Typical MOQ for Custom Stepper Motors
I. Product Perspective: Understanding MOQ & Product Factors
1. What does MOQ mean for custom stepper motors?
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) refers to the smallest number of custom stepper motors a manufacturer is willing to produce per order.
2. Why do custom stepper motors usually have an MOQ?
Custom motors require special tooling, winding changes, material sourcing, and testing, which increases production setup costs.
3. What is the typical MOQ for custom stepper motors?
The typical MOQ ranges from low quantities for minor modifications to higher quantities for fully customized designs.
4. How does customization level affect MOQ?
Minor changes like shaft length or cable type usually require a lower MOQ, while new tooling or windings increase MOQ.
5. Does motor size affect MOQ requirements?
Yes, smaller motors may have lower MOQs, while large or high-torque stepper motors often require higher MOQs.
6. Is MOQ different for open-loop and closed-loop stepper motors?
Closed-loop stepper motors often have higher MOQs due to encoder integration and additional electronics.
7. Can prototype or sample motors be ordered before MOQ?
Yes, many manufacturers offer prototype or sample production prior to mass production.
8. How does MOQ impact unit price?
Lower MOQs usually result in higher unit costs due to setup and material expenses.
9. Are MOQs the same for standard and custom stepper motors?
Standard motors often have no MOQ or very low MOQ, while custom motors require a defined MOQ.
10. Can MOQs be negotiated with stepper motor manufacturers?
Yes, MOQs are often negotiable depending on long-term demand, order frequency, and project potential.
II. Factory Customization Capability: OEM & Manufacturing Considerations
11. What types of customizations increase MOQ the most?
Custom tooling, special laminations, non-standard housings, and unique windings typically increase MOQ.
12. Do shaft and connector customizations affect MOQ?
Simple shaft or connector changes usually have low MOQ requirements.
13. Can manufacturers combine multiple variants to meet MOQ?
Yes, some factories allow mixed variants under one project to reach MOQ.
14. Are there different MOQs for prototype and mass production?
Yes, prototype runs usually have lower quantities but higher unit costs.
15. Can custom stepper motors be produced in small batches?
Yes, many factories support small-batch production for startups and R&D projects.
16. How do factories reduce MOQ for new customers?
By using existing platforms, shared tooling, or modular motor designs.
17. What information helps reduce MOQ requirements?
Clear specifications, long-term forecasts, and standardized components help reduce MOQ.
18. How long does it take to produce custom stepper motors?
Lead time depends on customization level, but prototypes are usually completed within several weeks.
19. Are custom stepper motors tested differently than standard motors?
Yes, they undergo additional validation, performance testing, and application-specific verification.
20. How does factory flexibility benefit OEM buyers regarding MOQ?
Flexible factories help OEMs reduce risk, control costs, and scale production efficiently.
English
العربية
Français
Русский
Español
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
ພາສາລາວ
ភាសាខ្មែរ
Bahasa Melayu
ဗမာစာ
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
עברית
Latine
Dansk
Shqip
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
Azərbaycan dili
Български
Català
































